- el dispositivo de eye tracking
- la fotografía de prensa
- las redes sociales, concretamente en Facebook.
Uno de ellos hace un recorrido por lo que se ha publicado, el otro hace un estudio con usuarios. Comparto aquí el resumen y la referencia:
Arrazola, Víctor; Marcos, Mari-Carmen (2014). Fotografía de prensa y redes sociales: la técnica de eye tracking. Ámbitos. Revista Internacional de Comunicación, 27.
El artículo presenta la técnica del seguimiento de la mirada (eye tracking) y analizalos estudios previos que, basándose en esta técnica, se han realizado sobre la prensa en las redes sociales, con especial detenimiento en Facebook. El artículo también hace un recorrido por el papel de la imagen en la prensadesde los inicios del fotoperiodismo hasta la aparición del periodismo digital.Dela revisión bibliográfica realizada se desprende que existe un claro vacío de investigaciones que aborden un análisis conjunto de las imágenes y las redes socialeshaciendo uso de la técnica del seguimiento de la mirada.
Cárcamo, Luis; Marcos, Mari-Carmen; Cladellas, Ramon; Castelló, Antoni (2015). News photography for Facebook: effects of images on the visual behaviour of readers in three simulated newspaper formats. Information Research, vol. 20, n.1.
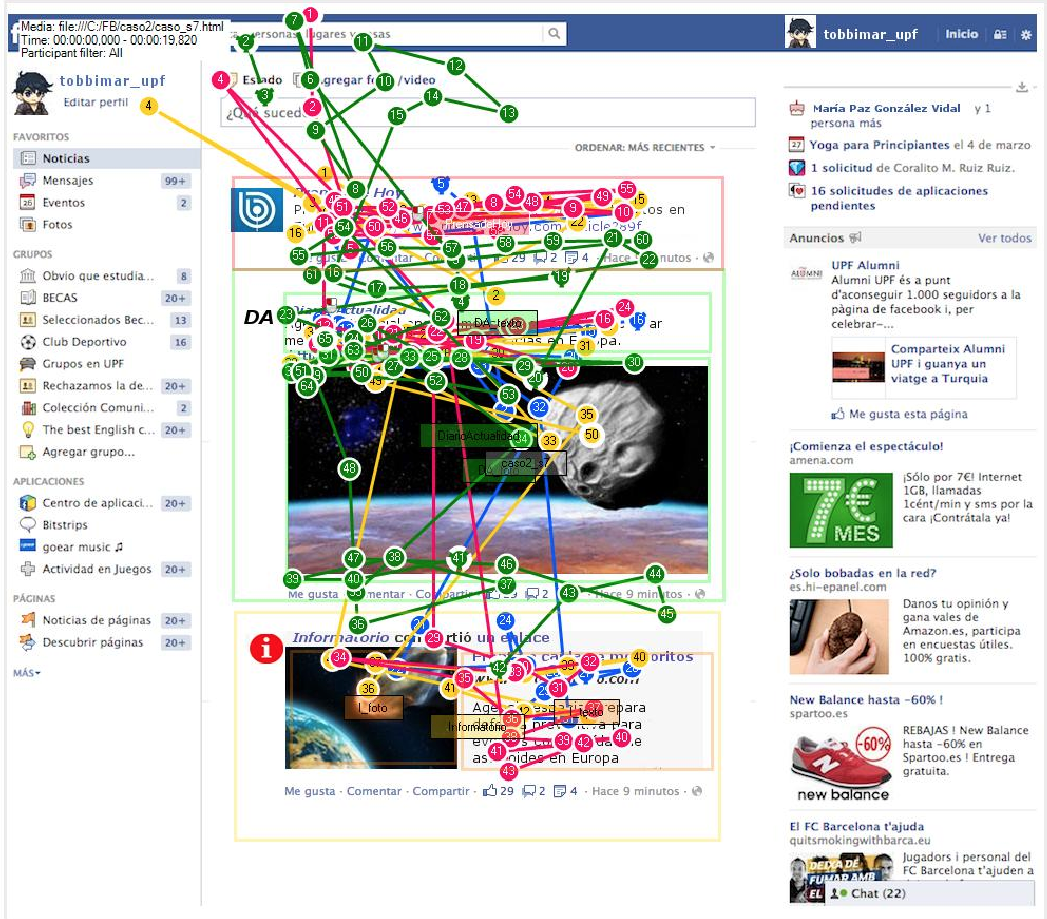
Introduction. The social networks have changed the news media scene and the media are striving to adapt to this new space by posting news that is attractive to their users. On Facebook in particular, the inclusion of images in news posts is very important, as they compete with the images depicting the users’ personal interests and those of their social circle.
Method. An empirical study was applied in which twenty-four users (Spanish university students) were shown three Facebook walls with news presented in three different formats according to the presence or absence of images and the size of these images. The experiment was recorded with an eye tracking device that tracked the movement of the users’ eyes.
Results. As the size of the images in the news posts varied, we found significant differences in the amount of time people took to start looking at each post, as well as the length of time their eyes remained on these posts. The post formats designed with larger images were looked at for a longer time and were clicked more often in order to read the news text. Generalization of these results must be restricted to the specific cultural context.
Conclusions. The size of the image in a news post presented on Facebook is extremely important in order to attract and retain readers. The scientific value of the study lies in researching visual behaviour in the consumption of news on Facebook.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario